Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Oba, Yojiro*; Nagakawa, Yoshiyasu*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Shibayama, Yuki; Ikeda-Fukazawa, Tomoko*
Carbohydrate Polymers, 327, p.121538_1 - 121538_11, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Applied)We describe non-toxic, tough nanocellulose (NC) hydrogels formed from chemically unmodified NC by cellulose crystalline transformation and subsequent freeze cross-linking reaction. Using low-concentration NaOH and freezing together induced the crystalline transformation of NC from cellulose I to II via freeze concentration. After the crystalline transformation, cross-linking between the NC and CA in the freeze concentration layer (FCL) provided a strong NC network structure, forming NC hydrogels with high mechanical strength. The freeze-cross-linked NC hydrogel easily retained powder adsorbents in its inner space by mixing the NC-NaOH sol and the powder, and the hydrogel showed high removal efficiency for heavy metals. The results highlight the versatility of chemically unmodified celluloses in developing functional materials, suggest possible practical applications.
Sekine, Yurina
Fain Kemikaru, 52(8), p.25 - 32, 2023/08
By using the freezing phenomenon, we discovered that a hydrogel with high compressive strength can be formed using only harmless materials, mainly carboxymethyl cellulose nanofibers. The key is the phase separation of ice crystals and solutes that occurs when aqueous solutions freeze. This paper describes the formation mechanism of the freeze crosslinked hydrogel and its properties.
Miura, Daisuke*; Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Oba, Yojiro; Hiroi, Kosuke; Ozawa, Tatsuhiko
Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications (Internet), 4, p.100251_1 - 100251_9, 2022/12
The reaction mechanism of carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMCF) hydrogel formed by freeze-crosslinking was investigated. We succeeded in observing the hierarchical structural changes during the freeze-crosslinking reaction. Freeze-crosslinked CMCF hydrogels exhibited a characteristic hierarchical alignment structure from the angstrom to micrometer scale that differed from normal cross-linked CMCF hydrogels produced by a conventional method without freezing. It was shown that the characteristic hierarchical structure contributes the excellent mechanical properties of freeze-crosslinked CMCF hydrogels.
Sekine, Yurina
Kata Gijutsu, 36(8), p.70 - 73, 2021/08
We developed a cross-linking method using freeze concentration and used it to synthesize a cellulose nanofiber hydrogel with high compressive strength. We will introduce the gelation mechanism and properties of the hydrogels in this article.
Yagi, Toshiaki
Dai-14-Kai Hoshasen Riyo Gijutsu Semina; Hirogaru Hoshasen No Sangyo Riyo Koen Tekisuto, p.67 - 72, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
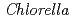
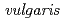
Ozaki, Takuo; Kimura, Takaumi; Onuki, Toshihiko; Yoshida, Zenko; Francis, A. J.
Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 22(11), p.2800 - 2805, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:45.2(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
Ozaki, Takuo; Kimura, Takaumi; Yoshida, Zenko; Francis, A. J.*
Chemistry Letters, 32(7), p.560 - 561, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.49(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Wach, R. A.*; Mitomo, Hiroshi*; Yoshii, Fumio; Kume, Tamikazu
Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 287(4), p.285 - 295, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:85.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
*;
JNC TN8430 2001-006, 65 Pages, 2001/10
We had been conducted to study hydraulic permeability along fracture intersection by NETBLOCK system using natural rock specimen. Since the permeability of this rock specimen fracture is high, it was suggest that turbulent flow might be occurred in available range of measurement system. In case of turbulent flow, estimated permeability and fracture aperture from test data tend to be low. Therefore we should achieve laminar flow. This study was used the high viscosity liquid instead of water, and test conditions which could attain laminar flow with the rock specimen was examined. The rock specimen is granite rock, has natural Y-type fractures intersection. A solution of Methyl-cellulose is used as high viscosity liquid. Due to the high viscosity liquid, hydraulic head could be measured in the wide range, and high viscosity liquid improved the accuracy of measurement. Laminar flow could be achieved in the rock specimen by the high viscosity liquid over 0.1wt%.
Yoshii, Fumio
Mizu, (612), p.16 - 22, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Yoshii, Fumio
Kombatekku, 28(12), p.32 - 35, 2000/12
no abstracts in English
Lam, N. D.*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu*; Kume, Tamikazu
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 59(4), p.393 - 398, 2000/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:68.65(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Yoshii, Fumio
Hoshasen Kagaku, 2000(70), p.12 - 19, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Yoshii, Fumio
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (87), p.55 - 58, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Kume, Tamikazu
JAERI-Conf 2000-003, p.87 - 93, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Wach, R. A.*; Mitomo, Hiroshi*; Yoshii, Fumio; Kume, Tamikazu
IAEA-SM-365, p.174 - 175, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Makuuchi, Keizo
Porima Daijesuto, 51(10), p.81 - 100, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Kume, Tamikazu; Nagasawa, Naotsugu*; Yoshii, Fumio; Tham, L. X.*; Hien, N. Q.*; Ha, P. T. L.*; Lam, N. D.*
Conference Proceeding RadTech Asia'99, p.475 - 480, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Kume, Tamikazu; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Ito, Hitoshi; Hashimoto, Shoji; *; M.R.Awang*; M.Lebaijuri*; Z.Othman*; F.Ali*; W.B.W.Husain*; et al.
JAERI-Research 98-013, 206 Pages, 1998/03
no abstracts in English